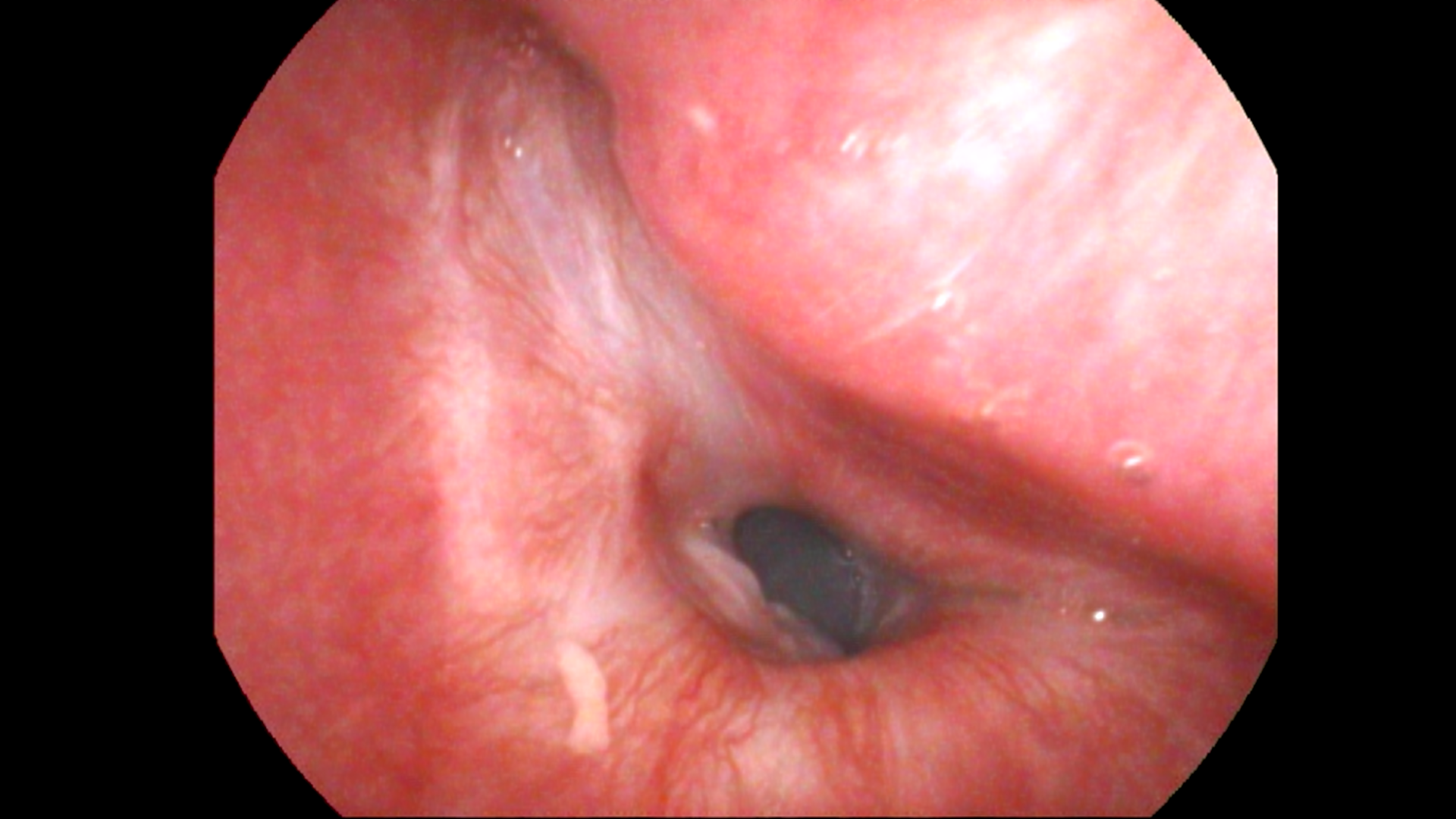
The human airway extends from the nostrils to the bronchi. It constitutes the nose, nasopharynx, oropharynx, larynx, trachea and bronchi. The larynx is further subdivided into glottis, supra-glottis and sub-glottis. Any problem that compromises the airway can lead to respiratory issues. Some of these problems can be life threatening. Compromise of the airway from the larynx and below are relatively more dangerous and associated with higher mortality and morbidity. One of the more common compromises is in the form of laryngotracheal stenosis.

Compromised airway can occur in both adult as well as pediatric population. Some of the common causes in pediatric population are laryngomalacia, laryngeal webs, congenital sub-glottic stenosis, laryngeal clefts etc. Some of the more common causes in adults are laryngotracheal stenosis, bilateral vocal cord immobility and malignancies. A lot of patients of compromised airway need a tracheostomy bypass the obstruction. Maintaining a tracheostomy in a substantial physical as well as mental burden for the patient and relatives. Treatment of most of these procedures is surgical intervention. Surgeries can be single step procedure or may multiple procedure. These procedures are highly challenging and specialised surgeries and need dedicated centers. We have been seeing and treating patients of airway compromise since the last eighteen years. Approximately, 1500 airways patients have been treated in the center out of which 400 are of pediatric age group. However, a constant rise in the number of patient has made the inception of a dedicated airway center the need of the hour.
Over the years in DMH we have treated stenosis and other complicated airway disorders. Transoral airway surgery, laser surgery and open airway surgeries have been performed. But with the increasing number of patients the time has come to structure the efforts put throughout these years and set up a dedicate airway center. This Centre will be developed as a joint project under the guidance of Dr Sachin Gandhi (Deenanath Mangeshkar Hospital, Pune) and Dr Kishore Sandu (CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland).
The purpose would be to manage all patients of airway compromise both pediatric and adult. The center will have a dedicated team of in house as well as visiting airway surgeons, intensivists and anesthetists.
The goal would be to provide patients with a disease free/ tracheostomy free life.
Approximately, 1500 airways patients have been treated in the center out of which 400 are of pediatric age group over the span of last 18 years. We have gradually developed the facilities at the center and now the department is equipped with state of the art infrastructure
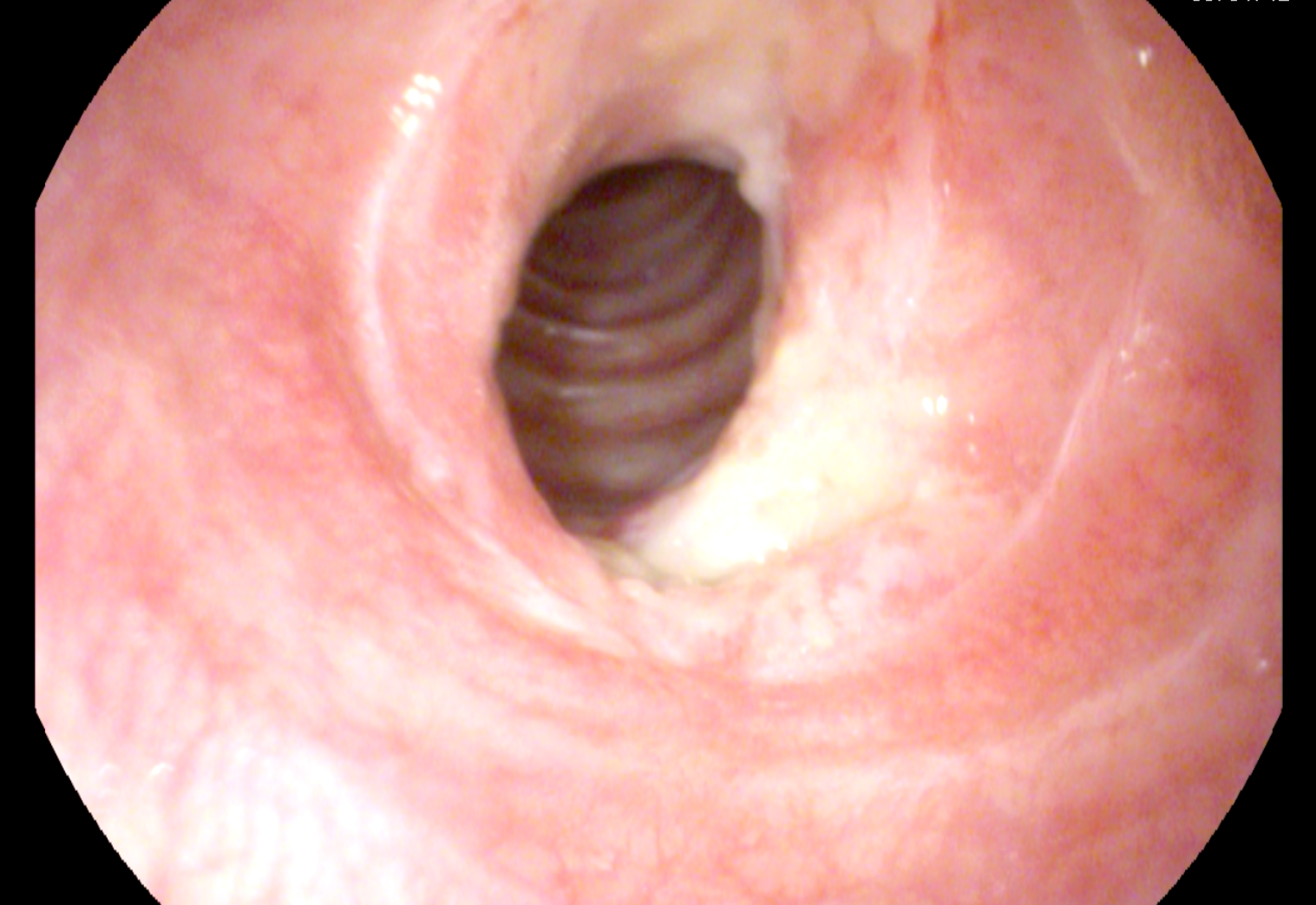
It is the procedure to treat tracheal stenosis. Tracheal stenosis is a narrowing of the trachea that causes breathing problems. Laser-assisted tracheal dilatation helps to remove the scar tissue that is causing the stenosis and dilate the airway. This procedure offers good results and provides substantial relief to the patients.
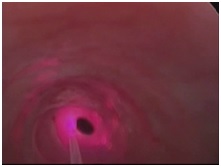
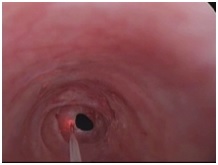


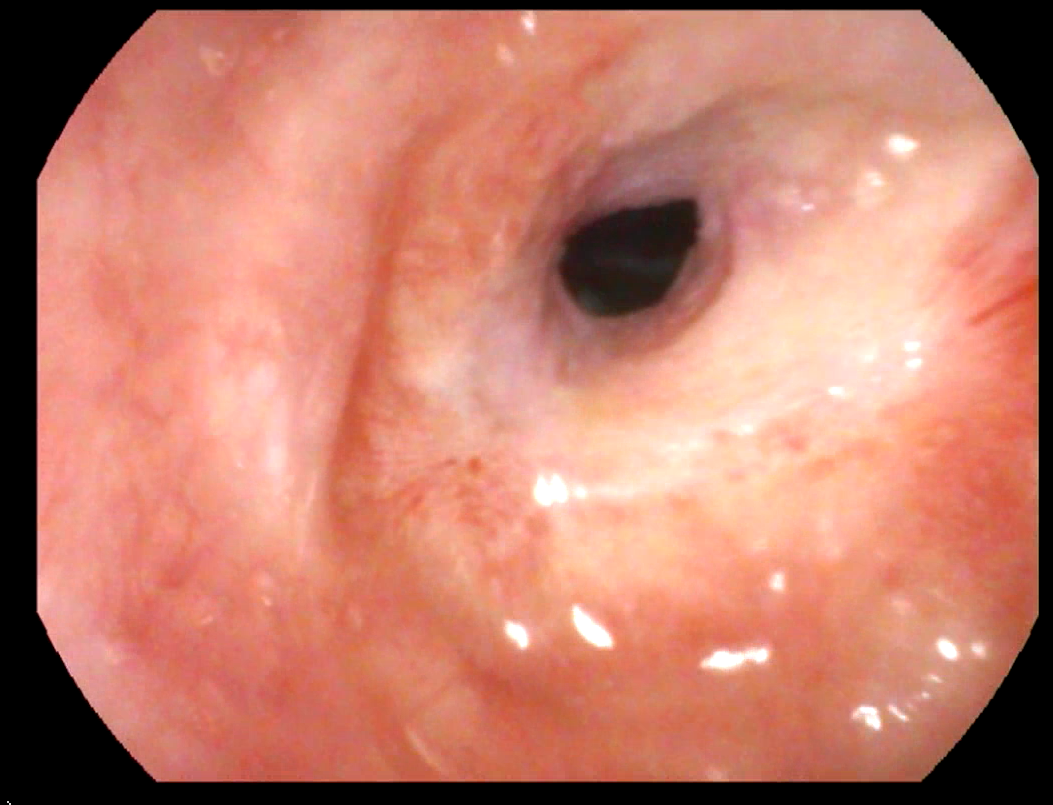
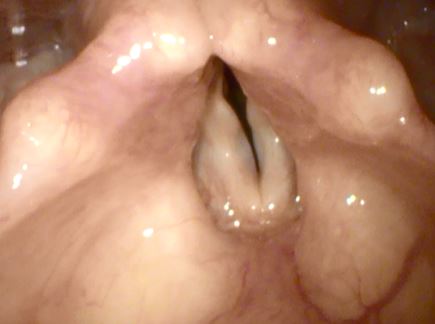
Patients having early breathing difficulty since 2-3 months only with uncertain prognosis for recovery; for example, breathing difficultydue topost radiotherapy complications or laryngeal trauma leading to crico-arytenoid joint fixation, are best treated with suture lateralization.A part of the back of one vocal fold(Posterior 1/3rd) is stretched and fixed away from the opposite vocal fold. This procedure helps regain the normal breathing of the patient, without disturbing the voice quality.

This procedure is done for the treatment of laryngomalacia. It is a congenital abnormality of the laryngeal cartilage resulting in collapse of the supra-glottic structures during breathing in, leading to airway obstruction. This is the most common cause of breathing difficulty found in newborn. The condition is self- recovering, but may be life threatening to few children. In such situation, diode laser-assisted supra-glottoplasty is the surgical treatment. In this procedure, the excessive floppy tissue of the voice box is trimmed in the operation room. This improves the breathing condition of the child.


Tracheal or laryngeal stenosis, which cannot undergo airway dilatation or not improving after multiple dilatations are recommended for tracheal reconstruction. In this procedure, the stenotic segment is excised and the normal ends of the trachea are brought together. This may also need grafts insertion depending on the condition of the patient.